Timber framing joints are critical connections in wooden structures, ensuring strength and durability. They combine traditional craftsmanship with modern engineering, offering both aesthetic and structural benefits while promoting sustainability.

Overview of Timber Framing
Timber framing is a traditional construction method using wood to create durable and aesthetically pleasing structures. It relies on precise joints to connect beams, ensuring strength and stability. Historically, this technique has been used globally, with modern applications adapting it for energy efficiency and sustainability. Timber framing emphasizes natural materials, minimizing environmental impact compared to concrete or steel. The joints are crucial, as they transfer loads and maintain structural integrity. Proper detailing and assembly prevent splitting, ensuring longevity. This method is valued for its blend of craftsmanship and functionality, making it a popular choice for eco-conscious builders. Its versatility allows for various designs, from residential homes to large-scale projects, while maintaining a reduced carbon footprint.
Importance of Joints in Timber Framing
Joints are the backbone of timber framing, ensuring structural integrity and load distribution. They prevent splitting and maintain frame stability, crucial for durability. Properly designed joints enhance strength, stiffness, and resistance to shear forces. They also allow for flexibility, accommodating natural wood movement. Without well-crafted joints, frames risk failure under stress. Their importance extends to both functionality and aesthetics, as visible joints often become decorative features. Detailed assembly and material selection are vital to prevent weaknesses. Joints must withstand environmental factors and long-term creep behavior, ensuring the structure remains safe and secure. In essence, the quality of joints directly impacts the overall performance and lifespan of a timber-framed building, making them indispensable in this construction method.

Historical Use of Timber Framing Joints

Timber framing joints have been used for centuries, with early examples found in ancient structures worldwide. These joints were crafted using hand tools and traditional techniques, emphasizing durability and precision. Historical joinery, such as mortise and tenon, was integral to constructing robust buildings like barns, bridges, and houses. Oriental joinery, as documented by Seike in 1977, showcased intricate designs that withstood environmental stresses. The historical use of these joints highlights their adaptability and effectiveness across cultures. Many traditional methods have influenced modern timber framing, blending heritage with contemporary engineering. The study of historical joints provides valuable insights into their long-term performance and aesthetic appeal, making them a cornerstone of both past and present construction practices.
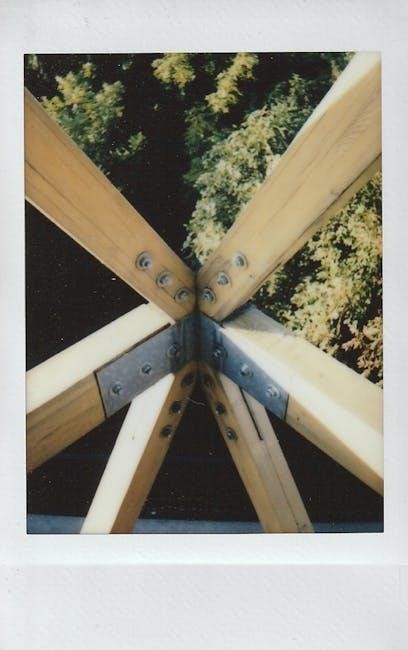

Types of Timber Framing Joints
Timber framing joints include mortise and tenon, housing, doweled, wedge, and tying joints. Each offers unique strength and flexibility, essential for traditional and modern construction techniques.
Mortise and Tenon Joints
Mortise and tenon joints are a cornerstone in timber framing, offering exceptional strength and durability. The tenon, a projecting piece, fits snugly into the mortise, a recessed area, creating a secure connection. This joint is highly resistant to shear forces, making it ideal for load-bearing applications. Proper detailing is crucial to prevent splitting, especially during wedge installation. Pegs are often used to reinforce the joint, though they don’t contribute to shear strength. The mortise and tenon joint is versatile, suitable for both traditional and modern constructions, and its visible end grain can add a decorative element. It remains a fundamental technique in timber framing, ensuring structural integrity and aesthetic appeal.

Housing Joints
Housing joints are a fundamental connection in timber framing, designed to securely join two pieces of wood. They consist of a recessed area (housing) in one piece, which accommodates the end of another piece, ensuring a flush surface. This joint is particularly useful in beam-to-post connections, providing excellent load-carrying capacity. Proper detailing is essential to prevent splitting, especially during assembly. Housing joints are often reinforced with pegs or wedges for added strength. Their design allows for even load distribution, enhancing structural stability. Historically, these joints have been integral to traditional timber frames, offering both functionality and aesthetic appeal. Modern applications continue to value their durability and versatility, making them a key element in sustainable construction practices.
Doweled Joints
Doweled joints are a popular connection method in timber framing, utilizing wooden dowels to secure two pieces of wood together. These joints are known for their simplicity and strength, making them ideal for various structural applications. The dowels act as rigid connectors, enhancing the joint’s shear strength and stability. Proper alignment and fit are crucial to ensure the joint performs effectively under load. Unlike pegged joints, dowels are not visible on the surface, providing a cleaner aesthetic. They are often used in both traditional and modern timber construction, offering excellent durability and resistance to structural stress. Doweled joints are particularly effective in scenarios where a flush surface is required, making them a versatile choice for craftsmen and builders. Their design ensures minimal material waste while maintaining high structural integrity.
Wedge Joints
Wedge joints are a traditional and effective method of securing timber connections, particularly in heavy framing. They involve driving a wedge, typically made of wood or metal, into a pre-cut slot to tighten the joint. This technique is often used in scenarios where settling or movement is anticipated, as the wedge allows for adjustment over time. Wedge joints are highly durable and resistant to shear forces, making them ideal for load-bearing applications. Proper detailing is essential to prevent splitting of the timber during installation. The simplicity of this joint, combined with its strength, has made it a favored choice in both historical and modern timber construction. Wedge joints are particularly useful in creating rigid and long-lasting connections in structural frames, ensuring stability and integrity under various loads.
Tying Joints

Tying joints are essential in timber framing for ensuring structural integrity and stability. They are designed to resist tension forces and prevent racking, making them critical in maintaining the frame’s rigidity. These joints are particularly important in scenarios where settling or movement is likely, as they help maintain alignment and tight connections. Tying joints often involve the use of pegs or other fasteners to secure the members together, ensuring a strong and durable connection. Proper detailing is crucial to avoid splitting and to ensure the joint can withstand various loads. Tying joints are especially vital in load-bearing applications, where failure could compromise the entire structure. Their simplicity and effectiveness make them a cornerstone in both traditional and modern timber construction, ensuring long-lasting and reliable connections in frames.

Design and Detailing of Timber Joints
Design and detailing of timber joints require careful consideration of material selection, joint geometry, and assembly methods to ensure strength and durability while preventing splitting.
Joint Detailing and Assembly
Joint detailing and assembly are crucial for ensuring the structural integrity of timber frames. Proper detailing prevents splitting during wedge installation, ensuring the tenon or spline remains intact. Pegs, while traditional, do not contribute to shear strength, emphasizing the need for precise joint design. Assembly requires alignment and tight tolerances to maintain frame stability. Detailed drawings and specifications from manufacturers guide the process, ensuring all components fit seamlessly. The visible end grain in joints can also serve as a decorative feature, blending functionality with aesthetics. Attention to detail in assembly ensures the frame withstands structural demands while maintaining its visual appeal, making joint detailing a cornerstone of successful timber framing projects.
Preventing Splitting in Joints
Preventing splitting in timber framing joints is essential for maintaining structural integrity. Proper wedge installation is critical, as improper techniques can cause the tenon or spline to split. Pegs are often used to secure joints, but they do not contribute to shear strength, highlighting the need for careful detailing. Tight joints and precise alignment are vital to avoid stress concentrations that could lead to splitting. Design details, such as the size and placement of wedges, must be carefully considered to distribute forces evenly. Material selection also plays a role, as certain woods are more prone to splitting than others. By adhering to proven methods and paying attention to assembly tolerances, splitting can be effectively minimized, ensuring the longevity and stability of the timber frame structure.
Material Selection for Joints
Material selection for timber framing joints is crucial for ensuring strength, durability, and structural integrity. The choice of wood species significantly impacts the joint’s performance, with factors like grain orientation, moisture content, and natural strength being key considerations. Hardwoods, such as oak, are often preferred for their durability and resistance to wear, while softwoods like pine may be used for their workability. Proper material selection also helps prevent splitting, as certain woods are more prone to this issue. The use of high-quality, well-seasoned timber ensures minimal warping and shrinkage, maintaining tight joints over time. Additionally, sustainable practices encourage the use of responsibly sourced materials, aligning with the environmental benefits of timber construction. Careful material selection enhances both the aesthetic and functional aspects of timber framing joints.
Structural Analysis of Timber Joints
Structural analysis of timber joints focuses on strength, stiffness, and durability. Engineering principles assess shear strength, joint stiffness, and creep behavior, ensuring safe and reliable timber frame designs.
Shear Strength of Joints
Shear strength in timber joints is a critical factor in ensuring structural integrity. It refers to the joint’s ability to resist deformation and failure under lateral loads. Factors such as the type of joint, material quality, and fastening methods significantly influence shear strength. For instance, mortise and tenon joints reinforced with pegs or bolts exhibit higher shear resistance compared to simple doweled connections. Probabilistic models and experimental testing are often used to assess shear strength, providing data for reliable design. Proper detailing, such as tight fits and alignment, enhances shear capacity. Additionally, the use of modern fasteners like bolts and dowels can improve performance. Understanding shear strength is essential for safe and efficient timber frame design, ensuring joints withstand anticipated stresses without compromising the structure’s stability or safety.
Joint Stiffness in Frame Analysis
Joint stiffness in frame analysis refers to the rigidity of connections within a timber structure, influencing its overall stability and load distribution. Stiffer joints resist deformation more effectively, enhancing the frame’s structural performance. The stiffness of sheathing-to-framing joints, for example, plays a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of the structure under various loads. Engineers often use finite element models to analyze joint stiffness, ensuring accurate predictions of how the frame will behave under stress. Proper detailing and material selection are essential to achieve optimal stiffness, minimizing unwanted movement and ensuring the structure remains stable. Accurate assessment of joint stiffness is vital for reliable frame analysis, as it directly impacts the safety and durability of the timber construction. By understanding and optimizing joint stiffness, engineers can create more efficient and resilient structures.
Creep Behavior in Joints
Creep behavior in timber joints refers to the gradual deformation of wood over time under constant load, which can affect the structural integrity of the frame. Research indicates that creep in wedged joints does not significantly compromise their performance, as the deformation stabilizes without major loss of strength. However, understanding creep behavior is crucial for long-term durability, especially in load-bearing connections. Designers must account for potential movement to prevent excessive settling or misalignment. Studies suggest that proper joint detailing, such as tight fits and precise wedge installation, minimizes creep effects. While creep does not appear to negatively impact joint functionality, ongoing monitoring and maintenance are recommended to ensure the structure remains stable. This behavior highlights the importance of material selection and assembly techniques in timber framing.

Sustainability of Timber Framing
Timber framing is an eco-friendly construction method, offering a sustainable alternative to materials like steel and concrete. It reduces carbon footprints and enhances energy efficiency.
Environmental Benefits of Timber
Timber is a renewable and sustainable resource, offering significant environmental benefits. Unlike steel and concrete, it has a lower carbon footprint and requires less energy for production. Timber absorbs carbon dioxide during growth, acting as a natural carbon sink. Its durability ensures long-lasting structures, reducing the need for frequent replacements. Additionally, timber can be recycled or repurposed, minimizing waste. Sustainable forestry practices further enhance its eco-friendly profile, ensuring that timber remains a viable option for environmentally conscious construction. These factors make timber framing a preferred choice for those seeking to reduce their environmental impact while building durable and aesthetically pleasing structures.
Energy Efficiency in Timber Construction
Timber construction offers exceptional energy efficiency due to its natural thermal properties. Wood has a high thermal mass, storing and releasing heat slowly, which helps regulate indoor temperatures. This reduces the need for heating and cooling systems, lowering energy consumption. Additionally, timber framing allows for tight construction, minimizing air leaks and improving insulation performance. Modern timber techniques, such as advanced framing and high-performance insulation, further enhance energy efficiency. The use of sustainable timber also aligns with energy-efficient goals by reducing the carbon footprint of buildings. Overall, timber framing combines traditional craftsmanship with modern energy-saving solutions, making it a highly efficient choice for eco-conscious construction projects.
Carbon Footprint Reduction
Timber framing significantly contributes to carbon footprint reduction by utilizing a renewable resource with minimal environmental impact. Wood absorbs and stores carbon dioxide during its growth, acting as a natural carbon sink. When harvested responsibly, timber construction helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions compared to steel and concrete, which have high energy-intensive production processes. Locally sourced timber further minimizes transportation-related emissions. Additionally, durable timber structures require less frequent replacement, reducing long-term carbon emissions. Sustainable forestry practices ensure that timber remains a viable, eco-friendly option for construction. By choosing timber framing, builders can significantly lower a building’s carbon footprint while promoting a healthier planet for future generations.
Resources and Further Reading
Explore detailed guides like Historic American Timber Joinery and Timber Framing Joints PDF for comprehensive insights. Visit TheTradesmanChannel’s Amazon storefront for tools and materials;
A Timber Framing Joints PDF is an essential resource for craftsmen and engineers, offering detailed diagrams and explanations of various joint types. These documents often include step-by-step guides for constructing mortise and tenon, housing, and doweled joints, ensuring precision and durability. They also cover historical techniques, blending traditional methods with modern engineering principles. Many PDFs provide insights into material selection, joint detailing, and assembly processes to prevent splitting and ensure structural integrity; Additionally, they may discuss the environmental benefits of timber framing, such as its sustainability and energy efficiency. For practical applications, resources like Historic American Timber Joinery and TheTradesmanChannel’s Amazon storefront offer tools and materials to support timber framing projects. These PDFs are invaluable for both beginners and experienced professionals seeking to master timber framing techniques.
Historic American Timber Joinery
Historic American Timber Joinery provides a comprehensive look at traditional timber framing techniques used in early American construction. These methods emphasize handcrafted joints like mortise and tenon, housing, and doweled connections, which were essential for building durable and long-lasting structures. The resource highlights the importance of precision and craftsmanship, showcasing how historical joinery contributed to the structural integrity of timber frames. It also explores the aesthetic value of exposed joints, which became a decorative feature in many historic buildings. By studying these techniques, modern craftsmen can gain insights into sustainable and efficient construction practices. The document serves as a valuable reference for preserving traditional timber framing methods while adapting them to contemporary projects. Its detailed illustrations and explanations make it a must-have for historians and practitioners alike.
Modern Timber Framing Techniques

Modern timber framing techniques blend traditional craftsmanship with advanced technology to create durable and efficient structures. The use of CAD software and CNC machines allows for precise joint detailing and assembly, ensuring tight connections and minimal material waste. Automated tools have streamlined processes like cutting and drilling, enhancing accuracy and speed. Hybrid joints, combining traditional methods with modern materials like steel connectors, offer improved strength and versatility. These techniques emphasize sustainability by optimizing material use and reducing waste. Additionally, modern methods often incorporate energy-efficient designs, aligning with green building standards. Resources like timber framing joints PDF guides provide detailed insights into these contemporary practices, making them accessible to both professionals and enthusiasts. This evolution ensures timber framing remains a viable and innovative construction method for the future.


0 Comments