Teaching reading to English language learners requires tailored strategies to address their unique linguistic and cultural needs, ensuring they build fluency and comprehension for academic success.
1.1 Overview of the Importance of Reading for ELLs
Reading is a cornerstone skill for English language learners (ELLs), enabling them to access academic content, develop language proficiency, and connect with cultural contexts. Proficient reading skills are essential for ELLs to succeed in school and beyond, as they bridge communication gaps and foster critical thinking. Reading helps ELLs build vocabulary, understand complex texts, and engage with diverse perspectives. It also enhances their ability to participate in classroom discussions and complete assignments effectively. By mastering reading, ELLs gain confidence and the tools necessary for lifelong learning and academic achievement.
1.2 Brief History and Evolution of Reading Instruction for ELLs
The instruction of reading to English language learners has evolved significantly over time, adapting to changing educational theories and cultural needs. Early approaches often focused on phonics and rote memorization, while modern methods emphasize comprehension, cultural relevance, and student-centered strategies. The 20th century saw a shift toward integrating language acquisition theories, recognizing the importance of linking reading to learners’ backgrounds. Recent advancements incorporate technology, differentiated instruction, and inclusive practices, ensuring reading instruction is tailored to diverse learner needs and promotes academic success.
Challenges Faced by ELLs in Reading
ELLs face challenges like limited vocabulary, cultural references, first language influence, and motivation issues, requiring tailored strategies for effective reading development and academic success.
2.1 Limited Vocabulary and Linguistic Challenges
ELLs often struggle with limited vocabulary and linguistic differences, impacting reading comprehension and fluency. Unfamiliar words and complex sentence structures can hinder understanding. Additionally, first language influence may lead to pronunciation or grammatical errors. Explicit instruction, word analysis, and contextual learning are effective strategies to address these challenges. Semantic mapping and technology-enhanced practice also support vocabulary development. By integrating these methods, educators can help ELLs build linguistic confidence and improve their reading skills, fostering academic success and bridging language gaps effectively.
2.2 Unfamiliar Cultural References and Background Knowledge
ELLs often encounter texts with cultural references and background knowledge unfamiliar to them, which can hinder reading comprehension. These gaps may lead to confusion and disengagement. Teachers can address this by previewing texts to highlight key cultural elements and providing explicit instruction on relevant background information. Graphic organizers and discussions can help students connect new information to their prior knowledge. Incorporating multicultural texts and diverse perspectives also fosters inclusivity and engagement. By bridging these cultural gaps, educators can enhance ELLs’ ability to interpret and relate to the material, promoting deeper understanding and active participation in reading activities.
2.3 First Language Influence and Transfer
English language learners often experience the influence of their first language when learning to read in English. This can manifest as positive transfers, such as applying familiar reading strategies, or negative transfers, like confusion due to differences in language structures or writing systems. Teachers should recognize these influences and address potential challenges, such as mispronunciation or grammatical errors. Leveraging students’ first language as a resource can enhance learning, while explicit instruction on English-specific features helps bridge gaps. Understanding this linguistic interplay allows educators to support ELLs more effectively in developing reading proficiency.
2.4 Motivation and Engagement Issues
Motivation and engagement are critical for ELLs’ reading development, yet challenges often arise due to language barriers, cultural differences, and lack of relevance in materials. ELLs may feel disconnected from texts that don’t reflect their experiences, leading to disengagement. Additionally, the stress of learning a new language can diminish confidence and motivation. Teachers can address these issues by incorporating culturally responsive practices, using multimedia resources, and providing opportunities for peer interaction. Creating a supportive environment and linking reading content to students’ interests and backgrounds can foster engagement and encourage active participation in reading activities.

Strategies for Improving Reading Comprehension
Effective strategies include pre-reading activities, graphic organizers, and peer discussions to enhance understanding. These methods help ELLs connect new content with prior knowledge and experiences.
3.1 General Instructional Strategies
General instructional strategies for teaching reading to ELLs include scaffolding techniques, explicit instruction, and connecting content to students’ cultural and linguistic backgrounds. Teachers should use pre-reading activities to build background knowledge and preview texts. Graphic organizers and visual aids help students organize information and make connections. Peer discussions and group work encourage active participation and collaboration. Incorporating technology, such as digital tools and multimedia resources, enhances engagement and provides additional practice opportunities. These strategies create a supportive learning environment, fostering both language development and reading comprehension skills tailored to ELLs’ diverse needs.
3.2 Using Graphic Organizers for Visualization
Graphic organizers are powerful tools for helping ELLs visualize and organize information, enhancing reading comprehension. Tools like Venn diagrams, concept maps, and story maps enable students to identify main ideas, supporting details, and relationships between concepts. These visual aids are particularly effective for ELLs, as they simplify complex texts and make abstract ideas more concrete. By using graphic organizers, teachers can help students build connections between new information and prior knowledge, fostering deeper understanding. Additionally, these tools support language development by providing a framework for expressing ideas clearly and coherently, making them adaptable to various proficiency levels and learning needs.
3.3 Incorporating Peer Discussion and Group Work
Incorporating peer discussion and group work into reading instruction can significantly enhance ELLs’ comprehension and language development. Collaborative activities allow students to share insights, clarify misunderstandings, and practice language skills in a supportive environment. Group work fosters scaffolding, where peers can assist one another in understanding complex texts. Teachers can structure discussions around open-ended questions or specific tasks, encouraging active participation. This approach not only promotes academic engagement but also builds confidence and reduces anxiety, helping ELLs feel more comfortable expressing their thoughts and ideas. Peer interactions also provide opportunities for authentic communication, reinforcing both reading and language skills simultaneously.

Vocabulary Development Techniques
Effective vocabulary instruction for ELLs involves explicit teaching, word analysis, and contextual learning. Using semantic mapping and technology-enhanced tools can deepen understanding and retention of new words.
4.1 Explicit Instruction and Word Analysis
Explicit instruction involves directly teaching vocabulary through clear definitions and examples, ensuring ELLs understand word meanings. Word analysis, such as breaking words into prefixes, suffixes, and roots, enhances decoding skills. Teachers should provide visual aids like word charts or diagrams to reinforce learning. Scaffolding techniques, such as modeling and guided practice, help ELLs grasp complex vocabulary. Incorporating student-friendly examples and contextual sentences makes instruction engaging. This approach not only builds vocabulary but also fosters independence in word recognition and comprehension, crucial for reading success.
4.2 Contextual Learning and Semantic Mapping
Contextual learning involves teaching vocabulary within meaningful sentences or passages, allowing ELLs to infer word meanings from context. Semantic mapping, a visual strategy, helps students organize words into categories or relationships, enhancing comprehension. For example, grouping words by themes like food or transportation aids retention. Teachers can use graphic organizers or mind maps to facilitate this process. This approach encourages active thinking and connects new vocabulary to prior knowledge, making learning more engaging and effective. Regular practice with contextual activities improves ELLs’ ability to understand and use vocabulary in reading and communication.
4.3 Technology-Enhanced Vocabulary Practice
Technology offers innovative ways to engage ELLs in vocabulary practice, making learning interactive and accessible. Digital tools like Quizlet, Kahoot, and Memrise provide gamified exercises, flashcards, and spaced repetition systems. Apps such as Duolingo and Babbel offer personalized lessons tailored to learners’ proficiency levels. Online platforms allow teachers to assign interactive activities, track progress, and provide immediate feedback. Multimedia resources, including videos and audio clips, enhance understanding by connecting words to visuals and contexts. These tools not only boost retention but also foster independent learning, enabling ELLs to practice vocabulary at their own pace, both in and out of the classroom.
Reading Comprehension Techniques
Effective techniques include pre-reading activities, during-reading strategies, and post-reading reflections to enhance understanding. Tools like graphic organizers and interactive texts support engagement and scaffolding for diverse learners.
5.1 Pre-Reading Activities and Previewing Texts
Pre-reading activities are essential for ELLs to build background knowledge and connect with the text. Strategies include previewing the text, discussing themes, and introducing key vocabulary. Using KWL charts (What I Know, What I Want to Know, What I Learned) helps activate prior knowledge. Graphic organizers and visual aids also support comprehension. Teachers can read aloud excerpts or summaries to familiarize students with the content. Setting clear reading purposes, such as identifying main ideas or characters, guides students and enhances focus. These activities create a foundation for meaningful engagement and reduce anxiety, making the reading process more accessible and effective for ELLs.
5;2 During Reading Strategies for Active Engagement
During reading, active engagement strategies are crucial for ELLs to stay focused and comprehend the text. Techniques like think-aloud protocols encourage students to verbalize their thoughts, identifying challenges and connections. Stop-and-jot methods involve pausing to write key points or questions, promoting reflection. Teachers can also use visual aids or graphic organizers to help students track plot, characters, or themes. Additionally, peer discussions or paired reading allow ELLs to collaborate, share insights, and clarify misunderstandings. These strategies ensure students remain engaged, develop critical thinking, and deepen their understanding of the text.
5.3 Post-Reading Reflection and Summarization
Post-reading reflection and summarization are essential for consolidating understanding and reinforcing learning. Teachers can guide students in reflective discussions, encouraging them to connect the text to their experiences or prior knowledge. Summarization activities, such as writing a concise paragraph or creating a visual summary, help ELLs synthesize key ideas. Additionally, exit tickets or reflective journals allow students to articulate their thoughts and questions. These strategies not only enhance comprehension but also provide teachers with insights into students’ understanding, enabling targeted feedback and support.

Role of Technology in Reading Instruction
Technology enhances reading instruction for ELLs by providing interactive tools, multimedia resources, and personalized learning experiences, fostering engagement and improving comprehension through innovative and accessible platforms.
6.1 Digital Tools for Reading Practice
Digital tools like online reading platforms, interactive e-books, and language-learning apps provide ELLs with engaging and accessible ways to practice reading. These tools often include features such as text highlighting, audio support, and instant feedback, which help learners build fluency and comprehension. Platforms like Duolingo, Khan Academy, and Reading A-Z offer tailored exercises and progress tracking, enabling personalized learning. Additionally, multimedia resources such as videos and podcasts complement traditional texts, making reading practice more dynamic and relevant. These tools are particularly effective for ELLs, as they can be used in both classroom and home settings, catering to diverse learning needs and proficiency levels.
6.2 Multimedia Resources and Interactive Texts
Multimedia resources and interactive texts enhance reading instruction for ELLs by combining visuals, audio, and hands-on activities. Videos, images, and interactive elements make complex texts more accessible, catering to diverse learning styles. Tools like interactive e-books and digital stories provide opportunities for ELLs to engage with content in meaningful ways, fostering comprehension and vocabulary growth. These resources also allow for differentiation, enabling teachers to tailor instruction to varying proficiency levels. By integrating multimedia, educators create dynamic learning environments that support ELLs in developing both language and literacy skills effectively.
6.3 Online Platforms for Collaborative Learning
Online platforms for collaborative learning provide ELLs with interactive spaces to engage in reading activities, fostering teamwork and language development. These tools enable real-time feedback, peer discussions, and shared tasks, enhancing comprehension and fluency. Platforms like discussion forums, virtual classrooms, and collaborative reading apps allow students to interact with peers globally, broadening cultural perspectives. Teachers can track progress, provide immediate support, and adapt instruction to meet diverse needs. Such platforms not only promote academic growth but also build confidence and collaboration skills, essential for ELLs’ success in reading and overall language acquisition.
Cultural and Socio-Emotional Considerations
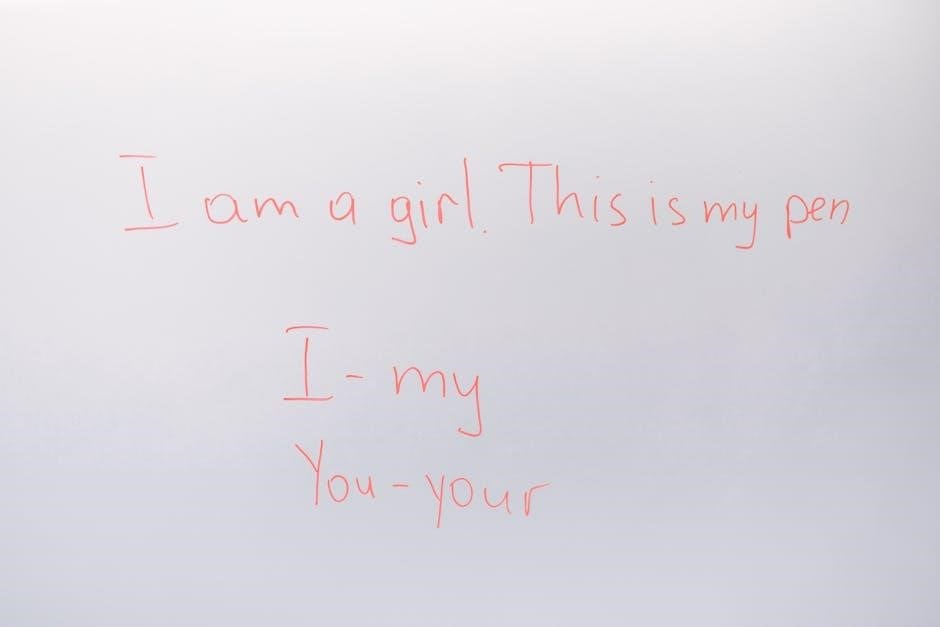
Cultural and socio-emotional factors significantly impact ELLs’ reading development. Creating an inclusive environment, addressing emotional needs, and integrating diverse texts help build confidence and engagement in learning.
7.1 Creating a Supportive Classroom Environment
Creating a supportive classroom environment is crucial for ELLs’ reading success. Foster respect, empathy, and cultural responsiveness by incorporating students’ backgrounds into lessons. Use visual aids and scaffolding techniques to build confidence. Encourage peer interactions and positive reinforcement to promote engagement. Provide opportunities for students to share their experiences, ensuring they feel valued and connected to the material. A safe and inclusive space helps ELLs overcome challenges and thrive academically and emotionally, laying a strong foundation for reading development and overall learning success.
7.2 Addressing Socio-Emotional Needs of ELLs
Addressing the socio-emotional needs of ELLs is vital for their reading development. Many ELLs face stress due to language barriers and cultural adjustments, which can hinder academic progress. Teachers should provide emotional support, create a sense of belonging, and foster resilience. Incorporating culturally responsive practices helps students feel connected to the curriculum. Encouraging open communication and active listening can build trust. Additionally, teaching coping strategies and promoting self-confidence empowers ELLs to navigate challenges. By prioritizing their socio-emotional well-being, educators create a nurturing environment that supports both their reading growth and overall emotional development.
7.3 Integrating Multicultural Texts and Perspectives
Integrating multicultural texts and perspectives enriches the reading experience for ELLs, fostering cultural connections and empathy. Using diverse texts, such as Shaun Tan’s The Arrival, allows students to relate to narratives reflecting their own or others’ cultural backgrounds. This approach validates their experiences and bridges language gaps. Multicultural texts also provide opportunities to discuss global themes, enhancing comprehension and critical thinking. By incorporating diverse voices, educators create an inclusive classroom environment that celebrates students’ heritage while promoting cross-cultural understanding. This practice not only supports reading development but also nurtures socio-emotional growth and a deeper appreciation for diverse perspectives.
Assessment and Feedback in Reading Instruction
Effective assessment and feedback are crucial for ELLs’ reading development. Using formative and summative methods, educators can monitor progress, identify gaps, and provide targeted, timely support.
8.1 Formative Assessment Techniques
Formative assessments are essential for monitoring ELLs’ reading progress and adjusting instruction. Techniques include exit tickets, think-pair-share, and running records to gauge comprehension and fluency. Exit tickets allow students to reflect on their understanding, while think-pair-share encourages peer discussion and reveals misconceptions. Running records provide insights into decoding skills and reading accuracy. Additionally, technology tools like quizzes and interactive activities offer immediate feedback, helping teachers identify learning gaps and tailor support. These methods ensure ELLs receive timely, targeted guidance, fostering continuous improvement in their reading abilities.
8.2 Summative Assessment Methods
Summative assessments evaluate ELLs’ reading progress at the end of a lesson, unit, or term. These include standardized tests, reading portfolios, and end-of-unit projects. They measure mastery of skills and comprehension, providing a comprehensive overview of learning. Standardized tests help compare performance across students, while portfolios showcase growth over time. Projects allow ELLs to demonstrate understanding through creative tasks. These methods ensure accountability and identify areas needing improvement, aligning with learning objectives and informing future instruction. They also provide clear, measurable outcomes for teachers and students to track progress effectively.
8.3 Using Technology for Ongoing Assessment
Technology enhances ongoing assessment of ELLs’ reading skills through digital tools and online platforms. These resources provide immediate feedback, track progress, and offer interactive exercises. Adaptive learning software adjusts difficulty based on performance, ensuring personalized practice. Online quizzes and reading games engage students while monitoring comprehension. Additionally, multimedia resources like audio and video texts support diverse learning styles. Technology also facilitates data collection, enabling teachers to identify learning gaps and tailor instruction. This continuous, data-driven approach ensures ELLs receive targeted support, promoting steady improvement in their reading abilities over time.

Differentiated Instruction for Diverse Learners
Differentiated instruction tailors reading lessons to meet diverse ELL needs, using strategies like learning centers, small groups, and scaffolding to support varied proficiency levels effectively.
9.1 Learning Centers and Small Group Instruction
Learning centers and small group instruction provide personalized reading practice for ELLs, allowing teachers to address diverse needs. These structured activities promote hands-on engagement, fostering phonics, vocabulary, and comprehension skills. Small groups enable targeted support, while learning centers offer independent practice, reinforcing concepts. Peer interaction in groups enhances language development and collaboration. Teachers can integrate technology and multimedia resources to make activities more engaging. This approach ensures ELLs receive tailored instruction, building confidence and fluency in a supportive environment. It also allows for cultural responsiveness, making learning relevant and meaningful for diverse learners.
9.2 Scaffolding Techniques for Complex Texts
Scaffolding techniques are essential for helping ELLs navigate complex texts. Strategies include pre-reading activities, such as previewing vocabulary and discussing background knowledge, to build foundational understanding. Teachers can break texts into manageable sections, using graphic organizers to visually map concepts. Sentence deconstruction and cloze activities further support comprehension. Scaffolding also involves gradual release of responsibility, where teachers model reading strategies before guiding student practice. These methods ensure ELLs actively engage with texts, fostering independence and confidence. By tailoring support to learners’ needs, scaffolding bridges gaps in vocabulary and background knowledge, enabling deeper understanding of complex material.
9.3 Adapting Instruction for Varied Proficiency Levels
Adapting instruction for ELLs with varied proficiency levels involves tailoring strategies to meet individual needs. Teachers can use tiered activities, where tasks are scaled according to difficulty, ensuring all learners are challenged appropriately. Leveled texts and digital tools allow for differentiated reading experiences, catering to diverse language skills. Incorporating visual aids, simplified language, and scaffolded support helps lower-proficiency students, while higher-proficiency learners can engage with more complex texts and independent tasks. Peer collaboration and feedback also foster a supportive environment, enabling students to learn from one another and progress at their own pace.

Parental and Community Involvement
Engaging parents and communities in ELLs’ reading development fosters collaboration and cultural connections. Workshops, volunteer programs, and shared reading activities empower families to support learning at home.
10.1 Tips for Engaging Parents in Reading Development
Engaging parents in ELLs’ reading development is crucial. Provide bilingual resources and host workshops to demonstrate effective reading strategies. Encourage parents to create a home reading environment, fostering daily practice. Offer tips on discussing texts and asking open-ended questions to deepen comprehension. Utilize technology, such as reading apps, to involve parents in their child’s progress. Highlight the importance of cultural connections by sharing multicultural texts. Ensure communication is accessible by providing materials in parents’ native languages. Collaborative efforts between teachers and families can significantly enhance ELLs’ reading skills and overall academic growth.
10.2 Fostering Partnerships with the Community
Fostering partnerships with the community is essential for supporting ELLs’ reading development. Schools can collaborate with local libraries, cultural centers, and organizations to access bilingual resources and multicultural texts. Community volunteers can provide tutoring or reading buddies, offering additional support. Partnerships can also facilitate access to technology and interactive reading tools; By engaging with community groups, educators can create culturally responsive reading programs that reflect students’ backgrounds. Such collaborations not only enrich learning experiences but also strengthen connections between schools and families, fostering a collective commitment to ELLs’ literacy growth and academic success.
Future Directions in Reading Instruction for ELLs
Future directions emphasize integrating AI, adaptive learning, and professional development to enhance ELL reading instruction, ensuring personalized and culturally responsive approaches for improved literacy outcomes.
11.1 Emerging Trends and Innovations
Emerging trends in teaching reading to ELLs include the integration of AI-driven platforms, adaptive learning technologies, and gamification to enhance engagement. These innovations provide personalized learning experiences, catering to diverse proficiency levels and learning styles. Additionally, the use of multimedia resources, such as interactive texts and videos, is becoming increasingly popular, allowing ELLs to connect visual and auditory cues with written content. These approaches not only improve reading comprehension but also foster cultural responsiveness by incorporating diverse perspectives and backgrounds into instructional materials.
Moreover, technology-enhanced vocabulary practice and real-time feedback tools are transforming how ELLs acquire and retain new language skills. These trends emphasize the importance of leveraging modern tools to create dynamic, inclusive, and effective reading instruction for ELLs.
11.2 The Role of AI and Adaptive Learning
AI and adaptive learning are revolutionizing reading instruction for ELLs by providing personalized, data-driven experiences. AI-powered tools analyze learners’ strengths and weaknesses, delivering tailored content that matches their proficiency levels. Adaptive learning platforms adjust in real-time, offering scaffolded support and immediate feedback, which enhances fluency and comprehension. These technologies also enable teachers to track progress and identify areas needing intervention. By integrating AI, educators can create dynamic, responsive learning environments that cater to the diverse needs of ELLs, fostering engagement and accelerating language acquisition. This approach bridges gaps in traditional instruction, making reading instruction more effective and accessible.
11.3 Professional Development for Educators
Professional development is crucial for educators teaching reading to ELLs, ensuring they stay updated on effective strategies and research-based practices. Workshops, coaching, and online courses provide teachers with tools to address diverse learner needs. Collaborative peer groups and mentorship programs foster shared knowledge and innovation. Professional development also emphasizes cultural responsiveness and the integration of technology. By enhancing their skills, educators can create inclusive, engaging reading environments that support ELLs’ linguistic and academic growth. Ongoing training ensures teachers are equipped to meet the evolving challenges of teaching reading to English language learners effectively.

Additional Resources and References
Recommended books include Reading, Writing, and Talk and Keys to Teaching Grammar to English Language Learners. Online forums and communities provide further support for educators.
12.1 Recommended Reading and Research
Key resources include Reading, Writing, and Talk: Inclusive Teaching Strategies for Diverse Learners and Keys to Teaching Grammar to English Language Learners. These texts offer practical strategies for improving reading comprehension and vocabulary development. Additionally, Teaching English Language Learners: Strategies that Work provides evidence-based approaches for classroom instruction. Online databases like ERIC and Google Scholar provide access to research articles on ELL reading instruction. These materials collectively support educators in creating effective, culturally responsive reading programs tailored to ELLs’ needs.
12.2 Online Communities and Forums for Educators
Online communities like EdSource and Purdue University’s Literacy Network Project offer valuable forums for educators to share strategies and resources for teaching reading to ELLs. These platforms provide access to expert lectures, research-based practices, and collaborative discussions. Educators can engage in real-time chats, access archived webinars, and exchange materials tailored to ELL reading instruction. Such forums foster professional growth and provide practical insights, enabling teachers to stay updated on innovative methods and best practices for supporting ELLs in achieving reading proficiency.


0 Comments